
Study the poem for one week.
Over the week:
Poems often adhere to specific poetic forms, defined as 'poems following distinct sets of rules.'
The nine poetic forms we'll study include the:
The haiku is 'a Japanese poem in three lines, the first and last consisting of five syllables, and the second consisting of seven syllables, usually with an emphasis on the season or a naturalistic theme.'
Traditional haiku rules are as follows:
Characteristics of traditional Japanese haiku poems include the following:
Activity 1: Recite the Poem Title, Poet Name, and Poem
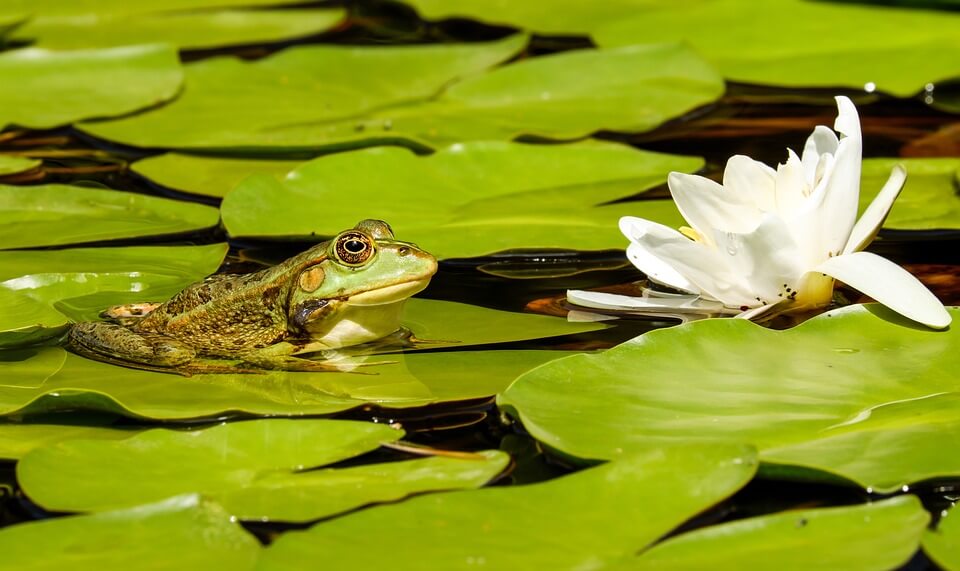
Activity 2: Study the Poem Picture
Study the poem picture and describe how it relates to the poem.

Activity 3: Narrate the Poem
Activity 4: Map the Poem
Activity 5: Complete Book Activities
